Organic Farming & why it is good for the environment
Agriculture has been and is a major component of the world economy since as long as we can remember. Over the years, in order to increase productivity of farming a lot of changes have taken place that have led to agriculture becoming more intensive, producing higher yields per acre by relying on greater chemicals use & technological inputs.
The whole process of Food production and consumption- from growing crops to processing, transporting, selling, storing and throwing away waste food – everything we eat has an impact on the environment & the climate. Agriculture is essential in sustaining human life. However, the practices associated with it off late have created certain impacts on the environment. On one hand, the intensification of agriculture has vastly increased productivity. On the other however, it has also had a number of potentially detrimental environmental consequences- ranging from climate change, deforestation, pollution, rapid erosion of fertile topsoils, contamination of drinking water supplies. These have been caused mostly by the chemicals used to enhance farmland productivity.

This brings us to the question:
What can we as a part of the Farming community do in a time when climate change, water shortages etc. threaten food production?
We can ensure Sustainability over the long term. This can be best done by sticking to Organic Farming practices.
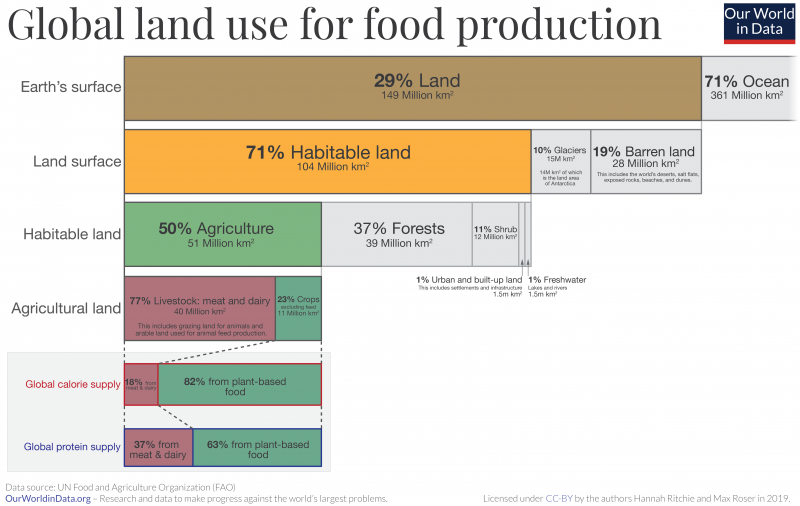
About half of the worlds habitable land is used for Farming. This means that it is not enough to ask only manufacturers & consumers to play their part. The food and farming systems must play its part as well in creating a healthy environment.Most environment changes observed occur slowly over time. One of the primary environmental concerns due to modern agriculture has to do with the chemicals we put on crops and the outcome of when those crops end up in the watershed. Organic agriculture considers the medium- and long-term effect of agricultural interventions on the agro-ecosystem. It aims to produce food while establishing an ecological balance.

How Organic farming is better for the environment:
Organic agriculture considers the medium- and long-term effect of agricultural interventions on the agro-ecosystem. It aims to produce food while establishing an ecological balance to prevent soil fertility or pest problems. Not just are Organics better for the environment, they are better for farmworkers as well because of not being exposed to the high levels of pesticides that are often used in conventional farming operations.
Air and climate change.
Organic agriculture does not use pesticides and herbicides thereby reducing non-renewable energy use by decreasing agrochemical needs. Many management practices used by organic agriculture like returning crop residues to soil, crop rotations, use of cover crops and integration of nitrogen-fixing crops, increase the return of carbon to the soil, raising productivity and favouring carbon storage. The more organic carbon is retained in the soil, the higher the chances of the mitigation potential of climate change through agriculture.
Soil.
Soil practices such as crop rotations, inter-cropping, symbiotic associations, cover crops, organic fertilizers and minimum tillage are central to organic practices; they help the soil stay healthy — rich in organic matter, nutrients and microbial activity. Pesticides and chemicals sprayed on plants contaminate the soil, water supply, and air; which is avoided through Organic agriculture. A large nine-year study by USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS), shows that organic farming builds up organic soil matter better than conventional no-till farming. These encourage soil fauna and flora, improving soil formation and structure and creating more stable systems.
The organic systems in the USDA test:
●Have more-fertile soil.
●Use less fertilizer and much less herbicide.
●Use less energy.
●Lock away more carbon in the soil.
Water.
One of the primary environmental concerns with modern agriculture has to do with the chemicals we put on crops and what happens when those crops end up in the watershed. In many agriculture areas, groundwater gets polluted with synthetic fertilisers and pesticides, which becomes a big problem. In Organic agriculture however, since the use of these is prohibited, they are replaced by organic fertilisers which enhances soil structure and water infiltration.
Biodiversity.
A Recent Study Reporting On A Meta-Analysis Of 766 Scientific Papers concluded that organic farming produces more biodiversity than other farming systems. The lack of pesticide use, attract new or re-colonizing species to the organic area, including wild flora and fauna and organisms beneficial to the organic system such as pollinators and pest predators.
Genetically modified organisms.
The use of GMOs within organic systems is not permitted during any stage of organic food production, processing or handling. The organic label provides an assurance that GMOs have not been used in the production and processing of the organic products. This is something which cannot be guaranteed in conventional products.

